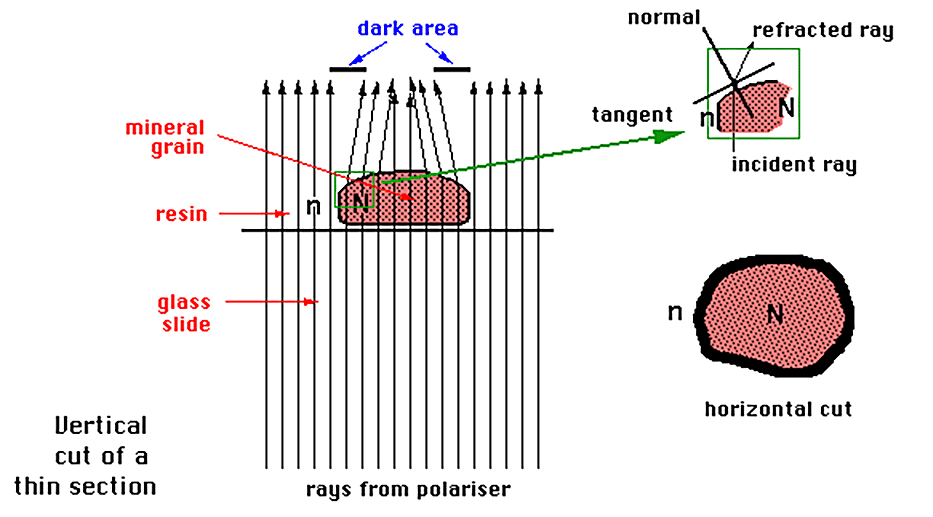
When a ray crosses the surface separating two mediums with a different refractive index with a certain degree of inclination, its path diverges.

In this case N>n, and the rays bend away from their optic normal (which is perpendicular to the surface which separates the two mediums) and are concentrated in the mineral, leaving a space which causes a dark area to appear on its edge.